External Loads on Pressure Vessel Supports
Specifying a wind or seismic code in COMPRESS directs it to perform a UG-22 analysis of the combined effects of pressure, weight, wind and seismic loads. But what about other global loads that commonly act on pressure vessels? Addressing these other types of loads is accomplished in COMPRESS by using the Loads Menu.
The COMPRESS Loads Menu allows designers to easily consider the effects of additional global external loads on pressure vessels. For the purposes of this discussion, global external loads are those loads other than pressure, weight, wind or seismic that produce general primary stresses in the pressure vessel supports. Similarly, local loads give rise to local stresses in individual pressure vessel components. Further information on how COMPRESS analyzes local loads can be found here.
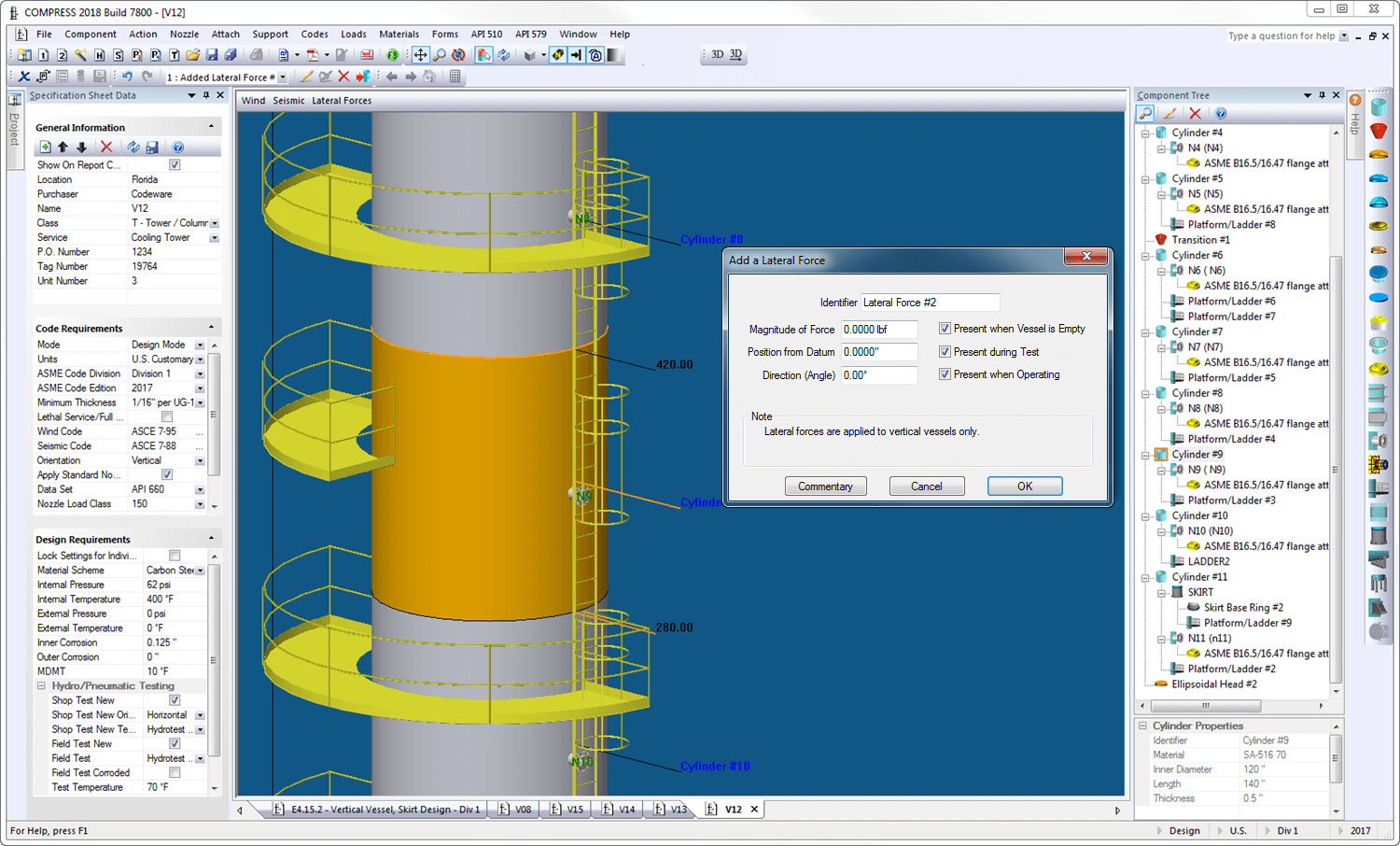
Global external loads in COMPRESS are broken down into two broad categories. The first, called a lateral force, is assumed to have no mass, does not add to the vessel’s weight and does not change its period of vibration. A common example of a global lateral force would be the piping load acting on a tower’s lower pipe support. The second is listed as a vertical load in the Loads Menu. Vertical loads do change the supported weight, often add an eccentric moment and change the equipment’s natural frequency, seismic and vortex shedding responses. A piece of equipment mounted directly on the pressure vessel, such as a reboiler, is a common example of a vertical load in COMPRESS. The COMPRESS Loads Menu feature:
Lets you specify as many lateral forces and vertical loads as you want
Allows you to specify if the load acts in one or all of the operating, empty and test cases
Combines the lateral forces and vertical loads with the loads due to pressure, weight, wind and seismic
Calculates the effects of the load combinations on pressure components such as cylinders and transitions
Determines the global external load’s effects on pressure vessel supports including skirts, legs and lugs
Calculates the external load’s effects on skirt base rings, leg base plates, anchor bolts and foundations
Increase Your Capabilities With COMPRESS



















UG-28 rules for external pressure design and vacuum rating.
























































+1 (941) 927-2670 | sales@codeware.com