Creep (Part 10) Damage Assessments Using INSPECT
Fixed Equipment in High Temperature Service (Creep)
Creep is a high temperature, time dependent failure mode that limits the life of stressed components. Creep failures commonly limit the useful life of heater tubes but can be the governing failure mode for any high temperature pressure vessel or pipe. The temperature at which creep becomes a concern depends on material and is generally around 700 degrees F. for carbon steels. ASME Code allowable (tensile) stresses consider creep by assuming a 100,000 hour service life and limiting the allowable stress such that creep deformation (strain) does not exceed 1%. Note also that the external pressure charts in the ASME Code do not consider creep buckling and are not used in these temperature ranges.
INSPECT and Part 10 Creep Damage Assessments
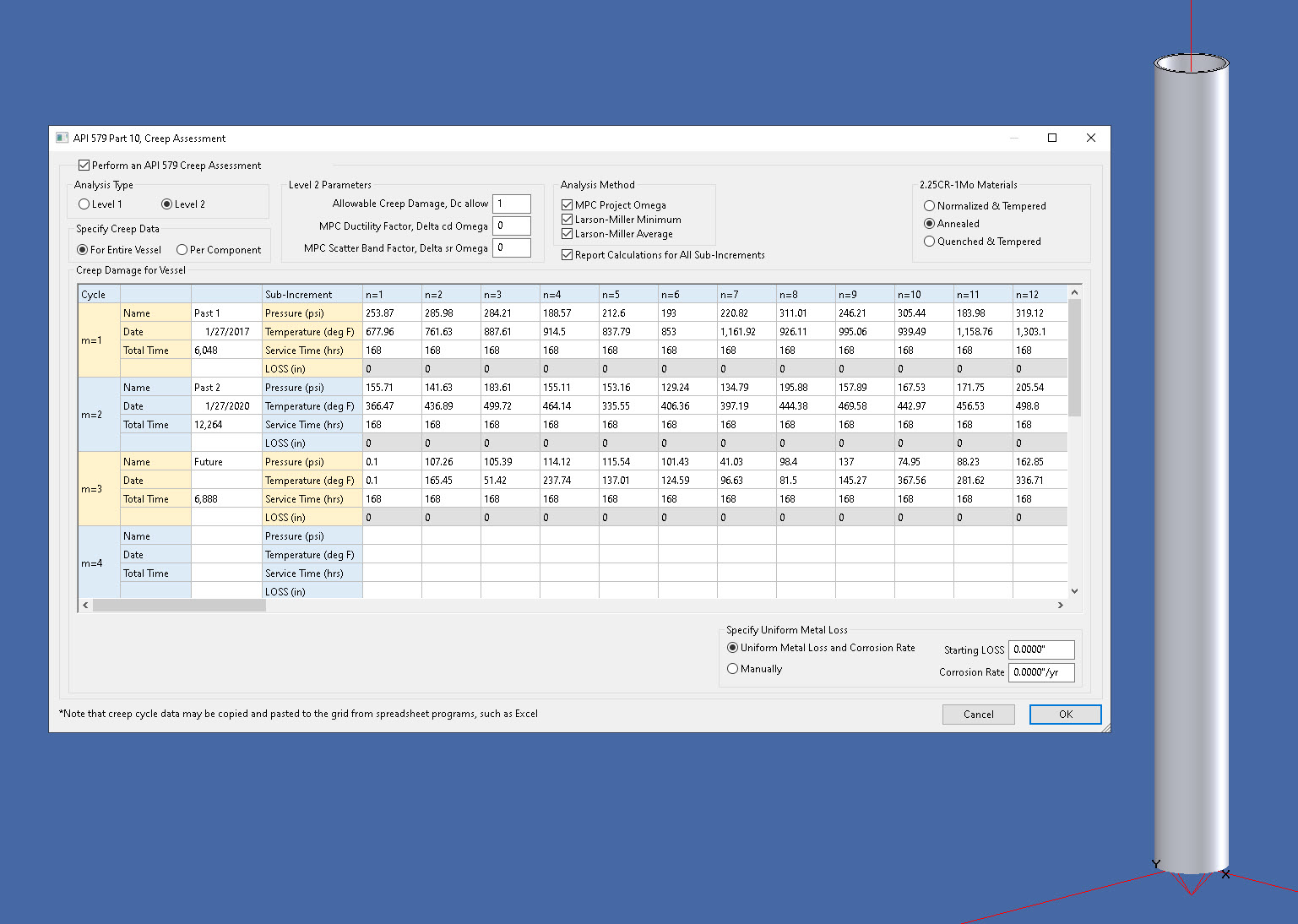
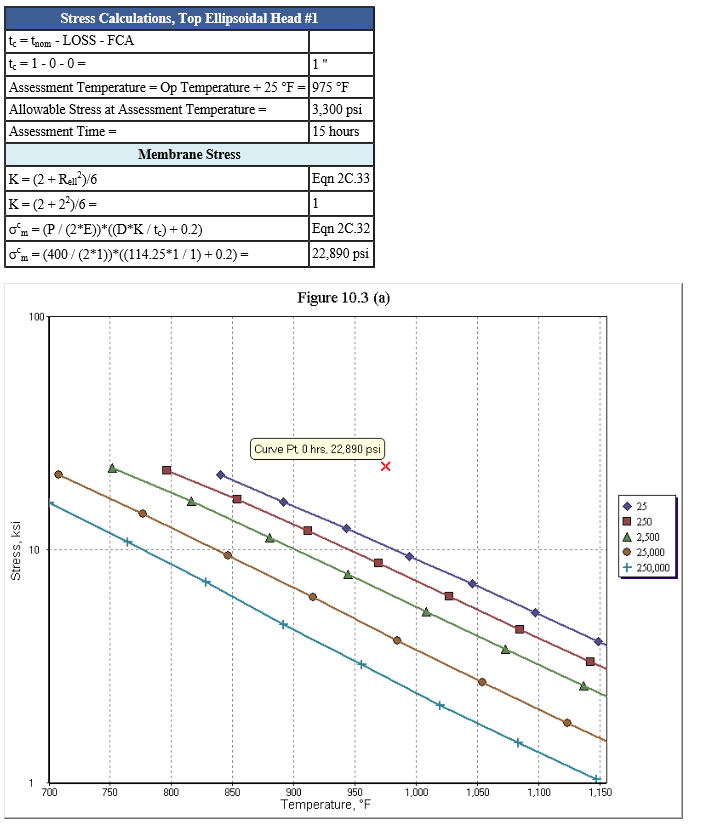
INSPECT makes performing Part 10 Level 1 and 2 creep assessments easy and fast. It provides a consistent means of recording equipment operating histories and calculations. All calculations are reported in detail along with any associated charts. In addition, you don’t need to spend your time moving information between programs manually to create reports. INSPECT’s all-in-one system creates professional looking, detailed reports with one button click.
Individual components or complete vessels can be modeled and assessed as required. A convenient creep summary report lists the components included along with applicable Pass/Fail conclusions. For Level 2 the MPC Project Omega, Larson-Miller Minimum, and Larson-Miller Average methods are available and can be run at the same time providing a very comprehensive report.
Performing API 579 Part 10 Creep Damage Assessments With INSPECT
More Information on Creep Can be Found at:
Creep and Creep Failures by The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors
Creep in Heater Tubes and Other Components by Inspectioneering
INSPECT Featured Capabilities