An Important Addition to ASME VIII-2: Class 1 Vessels
Beginning with the 2017 Edition of the ASME VIII-2 Code, it is now less expensive to build most medium size and larger carbon steel pressure vessels to Division 2, Class 1 instead of Division 1. Division 2 does this by introducing a new Class 1 vessel designation. Class 1 vessels use higher allowable stresses and more accurate design rules (equations) than Division 1 resulting in reduced wall thicknesses, nozzle reinforcement and welding.
A Comparison of Class 1 and Class 2 Vessels
The 2017 Edition of ASME VIII-2 now divides vessels into two classes, Class 1 and Class 2. The requirements for Class 2 vessels are largely unchanged from the previous 2015 Edition of ASME VIII-2. Class 1 vessels are new for 2017 and differ from Class 2 vessels as follows:
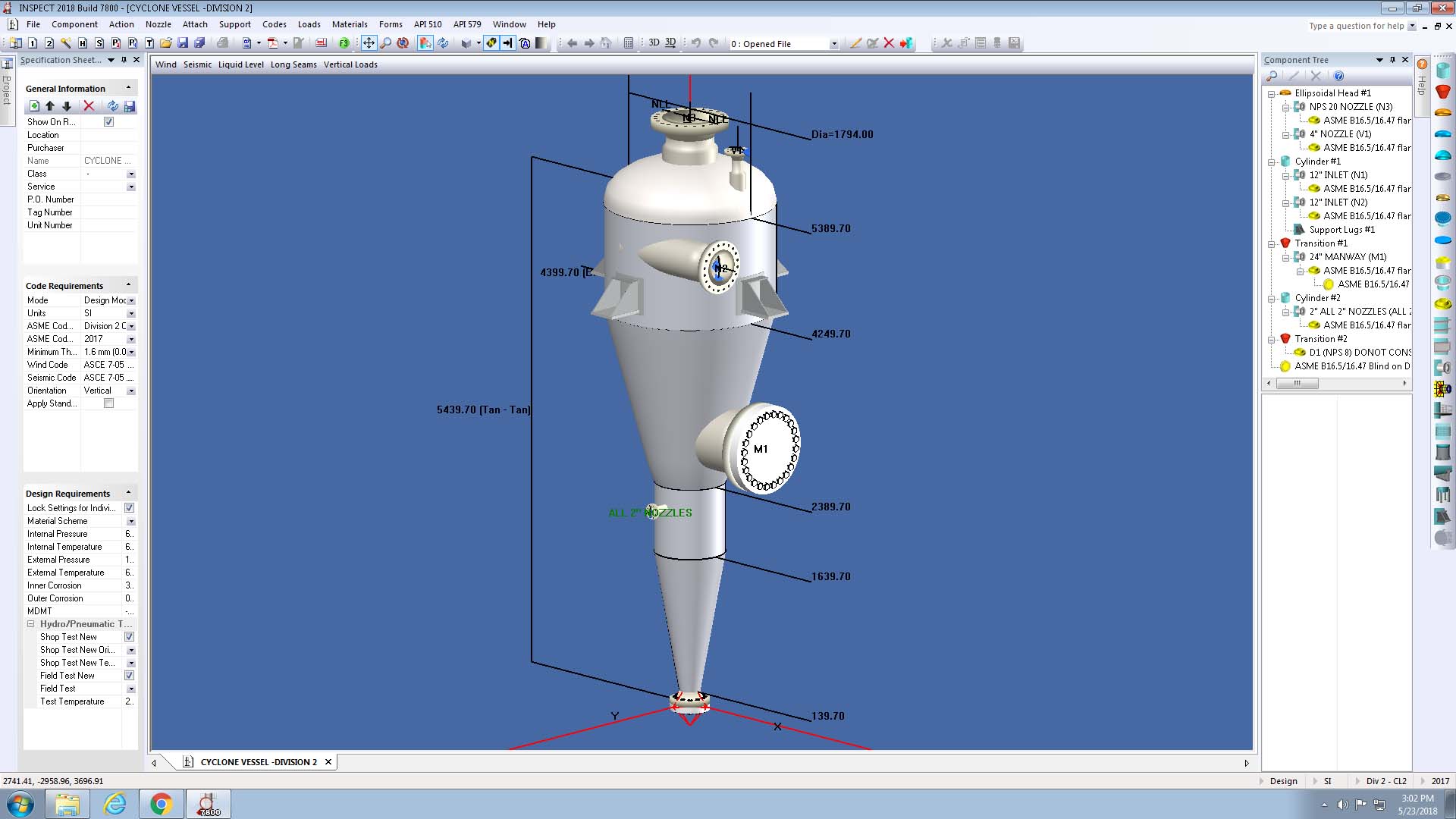
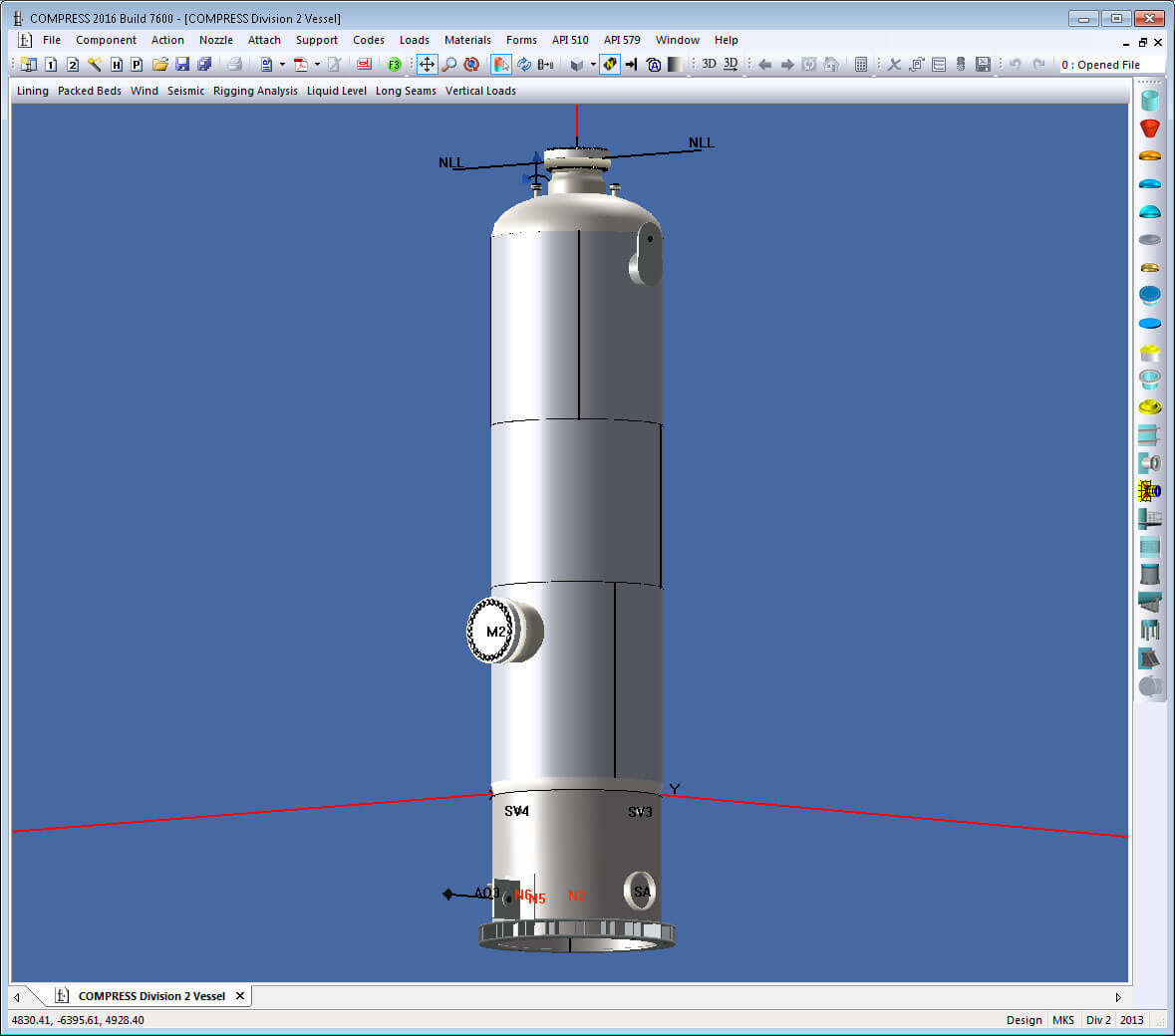
The new Class 1 vessel designation provides a way for “U” Certificate holders to build material saving Division 2 vessels without all of the additional overhead involved in producing full Class 2 vessels. For more information on obtaining an ASME Certificate of Authorization to fabricate ASME VIII-2, Class 1 vessels see Code Case 2891. The COMPRESS Division 2 option and INSPECT have been updated to include a Class 1 vessel design option.
ASME VIII-2 Versus ASME VIII-1 Cost Considerations
The overall cost reduction between Division 1 and Division 2 depends on answering the following question. Do the material and labor savings exceed the additional engineering, quality control and administrative costs? Historically, large, thick vessels have been good candidates for Division 2. The introduction of Class 1 vessels in the 2017 Edition of Division 2 gives more flexibility when deciding which Division is more cost efficient. Cost reductions are now available in more cases including carbon steel vessels with volumes larger than around 200 gallons (800 litres) designed for temperatures below 600 degrees F (315 degrees C). Division 2 also requires fewer reinforcing pads and allows thinner nozzle forgings resulting in additional cost savings. With the COMPRESS Division 2 Option you can switch between Divisions and Classes at any time. This makes it easy to determine which Division and Class produces the lightest, most economical vessel design.
How Does ASME VIII-2 Differ From ASME VIII-1?
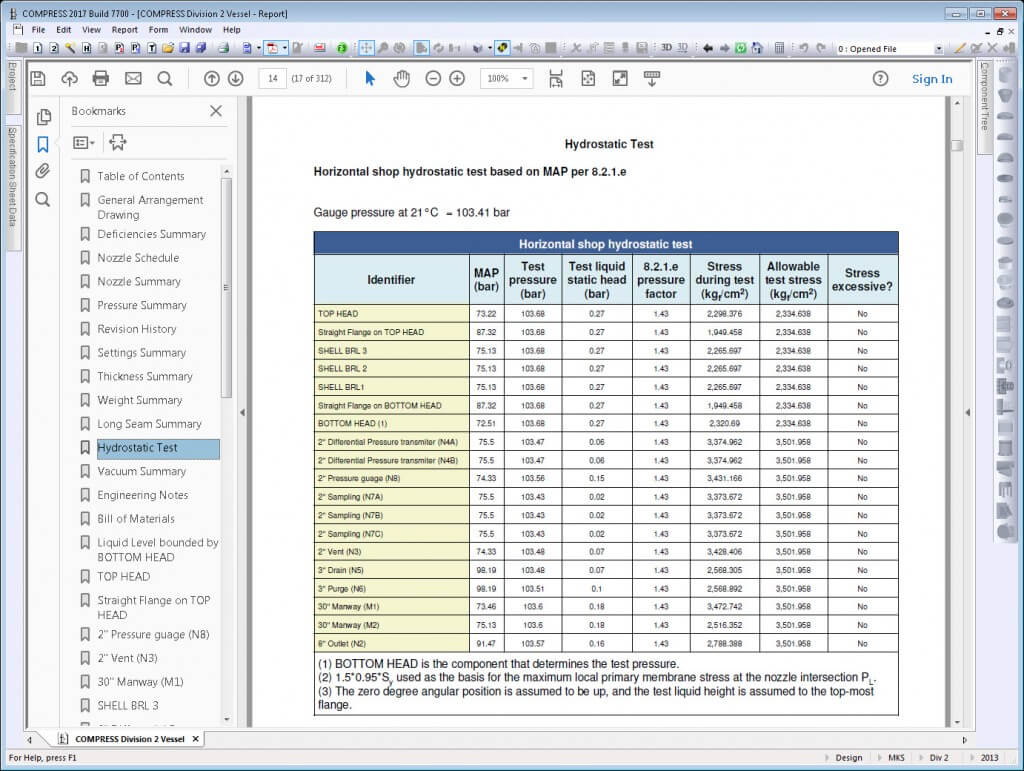
One of the main differences between Divisions 1 and 2 is that Division 2 uses lower design margins often resulting in higher material allowable stresses. Design margins are reduction factors applied to the material’s ultimate tensile strength (UTS) for the purpose of setting material allowable stresses in ASME II-D. The design margins are currently 3.5 for Division 1, 3.0 for Division 2, Class 1 and 2.4 for Division 2, Class 2. In Division 1, hydrotest stresses are not specifically limited and partial penetration nozzle welds are permitted. In Division 2, hydrotest stresses are limited so hydrotest stress calculations are mandatory and full penetration nozzle welds are required.
Another major difference is the theory of failure assumed and therefore the design equations used. Specifically, Division 1 uses the maximum principle stress theory while, starting with the 2007 Edition, Division 2 uses Von Mises. As a result, Division 1 uses two sets of design equations one for “thin” and another for “thick” vessels while Division 2 uses one set of equations for all vessel thicknesses. Of particular note are the more accurate nozzle design and allowable compressive stress (external pressure) rules in Division 2 both of which can provide additional savings.
In general, thinner Division 2 vessels retain safety factors that are comparable to thicker Division 1 vessels by incorporating more extensive engineering analysis and design requirements.